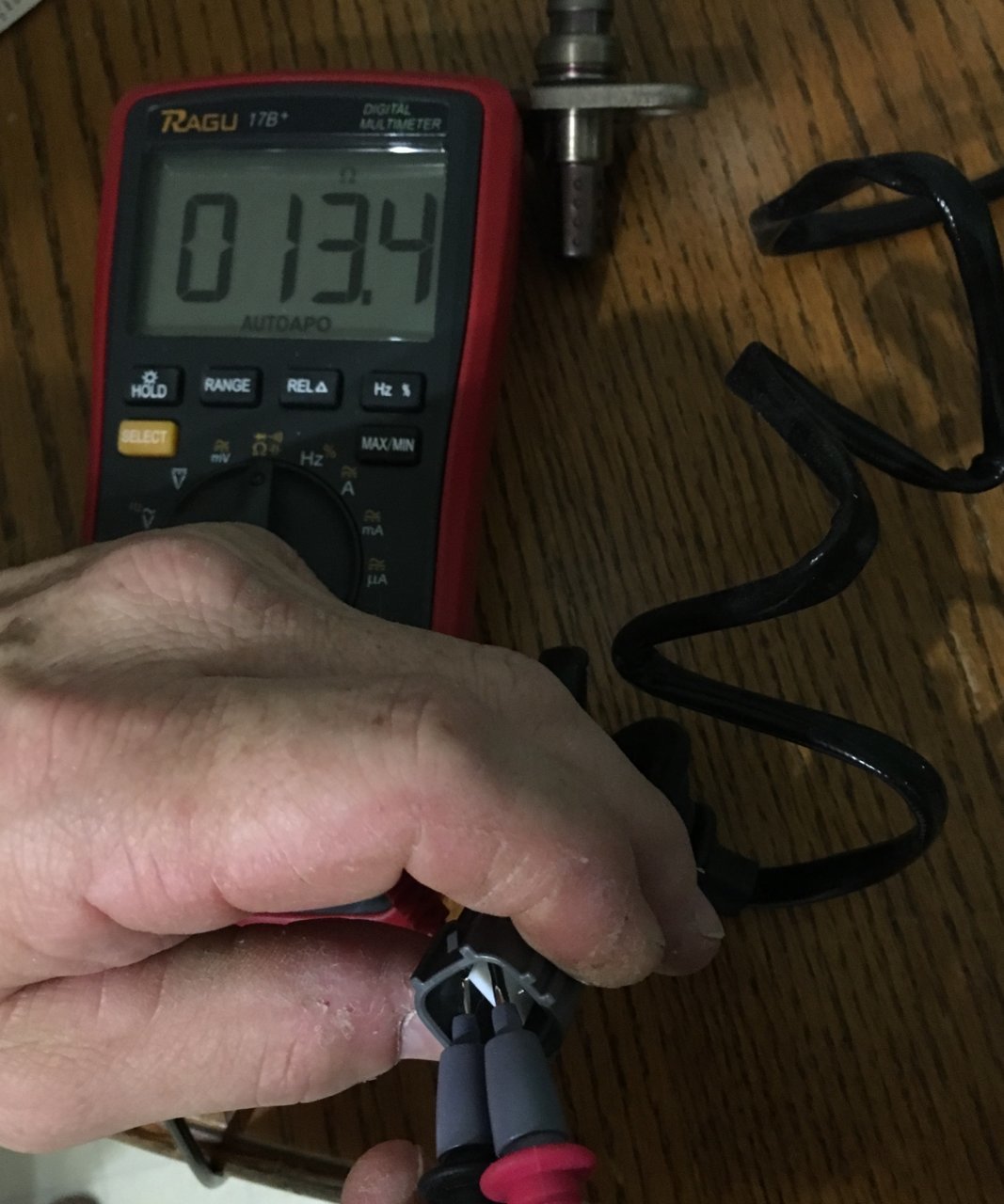
To test the O2 sensor in a Toyota, ensure the exhaust system is cold, switch on the clamp-meter to ‘DC current/DC amperage’ mode, clamp around the O2 sensor heater power wire, and start the engine. Testing the oxygen sensor in a Toyota involves using a clamp-meter to measure the voltage signals of the sensor.
It’s important to check for signs such as a check engine light, decreased fuel efficiency, a sulfur or rotten egg smell from the exhaust, black smoke emissions, and engine hesitation or power surges.
Additionally, a faulty MAF sensor can also cause rough engine performance, black smoke from the tailpipe, and abnormal fuel consumption, which can indicate O2 sensor problems in a Toyota vehicle.
Regular maintenance and testing of the O2 sensor can prevent further issues and ensure optimal vehicle performance.
Signs Of A Bad O2 Sensor In A Toyota
When it comes to testing the O2 sensor in a Toyota, there are a few signs that indicate it may be bad.
One of the first signs is the check engine light coming on. This is often the most noticeable indication that something is wrong with the sensor.
Another sign is a noticeable loss of fuel efficiency. If you find yourself filling up at the gas station more frequently, it could be due to a faulty O2 sensor.
Additionally, a sulfur or ‘rotten egg’ smell from the exhaust, black smoke from the exhaust, high emission levels, and engine hesitation or power surges are all signs of a bad O2 sensor.

How To Test An O2 Sensor With A Clamp-meter
Make sure the engine exhaust system is cold. Switch the clamp-meter to ‘DC current/DC amperage’ mode. Put the clamp around the oxygen sensor heater power wire. Turn the engine on.
How To Test An O2 Sensor With A Voltmeter
To test an O2 sensor with a voltmeter, start by connecting the voltmeter to the oxygen sensor to read voltage signals.
When connecting the voltmeter, ensure the engine exhaust system is cold and then switch the clamp-meter on to ‘DC current/DC amperage’ mode.
After that, put the clamp around either of the oxygen sensor heater power wires (but not both) and turn the engine on.
To confirm if your Toyota’s oxygen sensor is failing, connect your voltmeter to the oxygen sensor and read the voltage signals.
If you notice any issues such as the check engine light coming on, a noticeable loss of fuel efficiency, or a sulfur or ‘rotten egg’ smell from the exhaust, it could indicate a problem with the oxygen sensor.
Additionally, a faulty MAF sensor can cause your vehicle to run too rich or too lean, leading to symptoms such as black smoke from the exhaust, engine roughness, or frequent refueling.
You can also watch YouTube tutorials to understand how to test and replace an oxygen sensor or check its status on specific Toyota models.
How To Check And Replace An O2 Sensor
Testing and replacing an O2 sensor in a Toyota is a straightforward process that can be done at home with the help of a few tools. To test the sensor, you will need a multimeter.
Start by making sure the engine exhaust system is cold. Switch the multimeter to ‘DC current/DC amperage’ mode and put the clamp around either of the oxygen sensor heater power wires.
Then, turn on the engine and observe the readings on the multimeter. If the sensor is faulty, it needs to be replaced.
To replace the sensor, first, locate the old sensor near the exhaust manifold.
Disconnect the electrical connector and unscrew the sensor using an appropriate wrench. Install the new sensor by screwing it in and connecting the electrical connector.
Apply anti-seize to the threads of the new sensor to prevent future rusting and make it easier to remove in the future.
If the ‘check engine’ light is still on after replacing the sensor, you may need to delete the stored error codes using an OBD-II scanner or by disconnecting the battery for a few minutes. This should clear the codes and turn off the light.
Testing and replacing the O2 sensor in a Toyota is a simple task that can help improve engine performance and fuel efficiency.

Frequently Asked Questions For How To Test O2 Sensor Toyota
How Do You Test A Toyota O2 Sensor With A Multimeter?
To test a Toyota O2 sensor with a multimeter, follow these steps:
1. Ensure the engine exhaust system is cold.
2. Switch the multimeter to ‘DC current/DC amperage’ mode.
3. Place the multimeter clamp around one of the oxygen sensor heater power wires.
4. Start the engine.
5. Read the voltage signals on the multimeter connected to the oxygen sensor.
(Note: Ensure all steps are followed carefully and consult a professional if needed)
How Do You Test A O2 Sensor To See If It’s Bad?
To test an O2 sensor and see if it’s bad, follow these steps:
1. Ensure the engine exhaust system is cold.
2. Switch on the clamp-meter to ‘DC current/DC amperage’ mode.
3. Put the clamp around either of the oxygen sensor heater power wires.
4. Turn the engine on.
What Are Symptoms Of A Bad O2 Sensor?
Symptoms include check engine light, decreased fuel efficiency, rotten egg smell from exhaust, black smoke, high emissions, engine hesitation or power surges.
Conclusion
To ensure the proper functioning of your Toyota’s O2 sensor, testing it is essential.
From checking the engine exhaust system to using a clamp-meter, these methods will help you identify any issues with the sensor.
Remember to pay attention to signs like check engine lights, fuel inefficiency, and unusual exhaust smells. Regularly testing your O2 sensor will help you maintain your vehicle’s performance and efficiency.
